Introduction
Networking data centers are a critical infrastructure for modern businesses, serving as the backbone for various services and applications. These data centers often comprise a multitude of interconnected nodes to handle the routing and processing of network traffic.
In a data center fabric, the maintenance mode on spine and leaf devices needs to be activated quite often. During this mode, the traffic flowing through the device is drained out or rerouted to other devices so that you can perform maintenance activity like replacing line cards or fixing any issue on the device by removing a device from a production environment or taking a node offline temporarily for maintenance. This ensures the services running on the node are seamlessly transferred to other available nodes without causing any downtime for users. In general, this operation is called cost-out and cost-in. The ‘cost-out’ operation drains out the traffic and the ‘cost-in’ feeds in the traffic after the drain out.
This blog explains these operations in detail. Further, it explores how you can seamlessly achieve these with SONiC as NOS and using ONES-Orchestration as a tool.
Understanding Why Cost-Out And Cost-In Operation is Necessary in Data Centers Explore how draining plays a key role in maintaining data centers:
- Planned Maintenance: Data Centers require maintenance activities like hardware upgrades, software updates, or network reconfigurations. Draining allows administrators to take a device offline, transfer its workload, and perform maintenance tasks without affecting service availability.
- Capacity Planning: At times, data centers need to redistribute resources to optimize performance. Draining allows administrators to free up resources on specific devices by moving services and workloads to other devices with extra capacity. This helps in balancing the workload and avoiding resource bottlenecks.
- Faulty Device or Component Replacement: When a device or its components (such as a hard drive, power supply, or network interface) fail, it becomes necessary to replace/repair them. Draining allows a controlled migration of services from faulty device to the functional ones. Post the replacement/repair, the device is reintegrated into the production environment.
- Load Balancing: centers often employ load-balancing techniques to evenly distribute incoming requests and workloads across multiple devices. If a device becomes overloaded or experiences performance issues, administrators may decide to drain it to redistribute the workload to other devices. This helps to prevent service degradation/potential failures caused by an overloaded device.
- Scheduled Downtime: Sometimes, data centers undergo planned downtime for various reasons such as infrastructure upgrades, reconfigurations, or security patches. The draining allows a smooth transition of services to other active devices, ensuring users experience minimal or no interruption in service during the scheduled downtime.
How NetOps Achieve Cost-Out and Cost-In
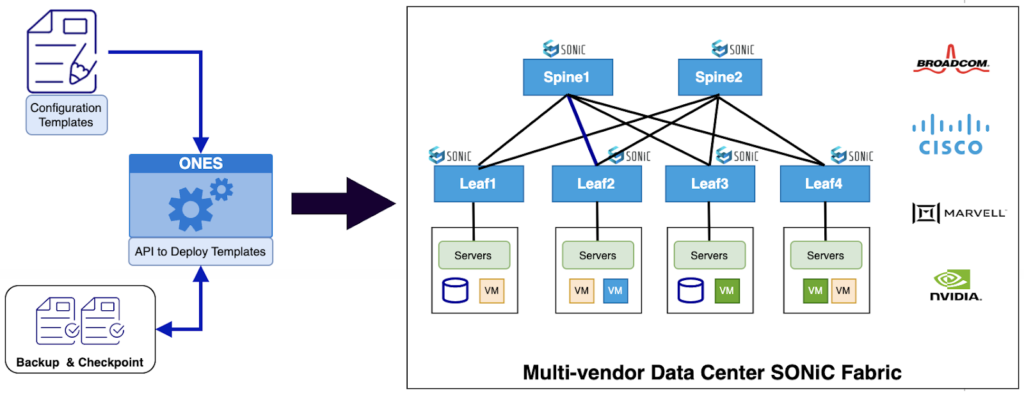
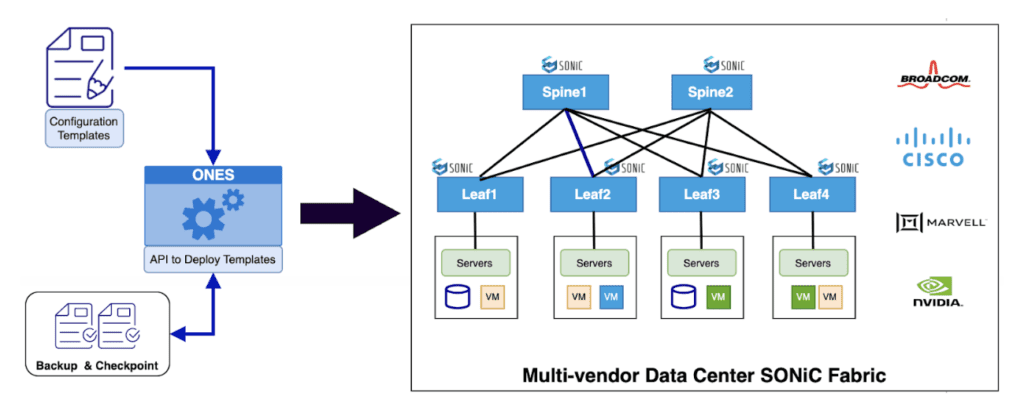
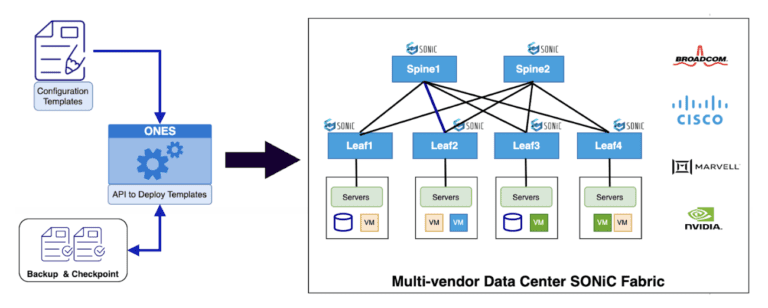
A Brief Overview of ONES and ONES-Orchestration
ONES is a networking solution to simplify and streamline NetOps for multi-vendor network automation and orchestration solutions.
Together, the ONES (Open Network Enterprise Solution) and ONES-Orchestration tools provide a comprehensive solution for managing and maintaining network infrastructure. They offer seamless integration with existing network equipment along with increased flexibility, scalability, network performance, reliability, and cost savings.
ONES-Orchestration Integration with SONiC Fabric
- Multi-Vendor Support: ONES Orchestration supports a wide range of networking equipment from different vendors, allowing organizations to build automated and orchestrated network solutions that can work with their existing infrastructure.
- Network Automation: ONES Orchestration provides tools and libraries for automating network operations such as configuration management, network provisioning, and change management.
- Orchestration: ONES Orchestration offers a platform for orchestrating network services such as routing, firewalling, and load balancing, across multiple devices and vendors.
- Integration with Popular Tools: ONES Orchestration can be integrated with popular network management and monitoring tools such as Ansible, Grafana, and Nornir—allowing organizations to leverage their existing toolsets and workflows.
ONES-Orchestration API for Cost-Out and Cost-In (Day 2 Use Case)
The ONES Orchestration is a Dockerized container capable of operating on x86 systems. It provides an API for performing soft provisioning and generating a difference. The very same API can be used to finally push/apply the configuration to the devices.
At the controller, this API will identify the delta and push the delta configuration back to the device in most cases without impacting forwarding, unless the changes themselves are disruptive. ONES Orchestration can be easily integrated into the existing NetOps workflow by giving intended configuration as input. Here’s the high-level diagram of the proposed ONES Orchestration tool and API interface.
The Ultimate Solution for Streamlining Your NetOps (Day-2 Use Case)
Implementation and Optimization
- Research about compatible switching hardware and choose the switches that meet your organization’s requirements
- Download and install SONiC on the chosen switches, following the provided installation packages and documentation
- Install ONES Solution on your server or virtual machine and integrate it with SONiC Fabric network
- Design and implement network automation and orchestration solutions using ONES Orchestration tools and libraries
FAQs
1-What is ONES Orchestration and how does it enhance SONiC fabric deployment?
ONES Orchestration is a powerful network automation and orchestration platform designed to work seamlessly with SONiC-based fabrics. It simplifies Day-2 operations like cost-out and cost-in through APIs, enabling automated provisioning, configuration management, and service orchestration across multi-vendor network environments dramatically reducing deployment time and operational overhead.
2-How does the cost-out and cost-in process work in SONiC-based data centers?
In SONiC environments, cost-out operations drain traffic from a device to prepare it for maintenance or upgrades, while cost-in reintroduces the device post-maintenance. Using ONES Orchestration, this process is automated via APIs, ensuring seamless traffic rerouting, zero-downtime service transitions, and error-free configuration updates across the network fabric.
3-Can ONES Orchestration integrate with existing NetOps tools like Ansible and Grafana?
Yes, ONES Orchestration is designed to integrate effortlessly with popular NetOps tools like Ansible, Grafana, and Nornir. This compatibility allows organizations to enhance their current automation workflows, visualize network health metrics, and orchestrate complex changes without overhauling their existing toolchains.
4-What are the key benefits of using ONES for multi-vendor network environments?
ONES offers robust multi-vendor support, real-time telemetry, and centralized visibility across different NOS platforms. It eliminates vendor lock-in, improves operational efficiency, and accelerates deployment cycles. With ONES Orchestration, NetOps teams gain scalable and flexible tools for managing complex infrastructures, reducing downtime and configuration errors.
5-How can enterprises get started with SONiC and ONES Orchestration for Day-2 NetOps?
To get started, organizations should select SONiC-compatible switches, install SONiC firmware, and deploy the ONES suite on a server or VM. Once integrated with the fabric, ONES Orchestration APIs can be used to automate Day-2 tasks such as device draining, configuration deltas, and service provisioning—laying the foundation for agile and efficient NetOps.
6. How does ONES Orchestration perform configuration changes without disrupting traffic?
ONES Orchestration uses a delta-based API approach that identifies only the required configuration changes and pushes them to devices. In most cases, this soft provisioning occurs without impacting traffic forwarding, unless the changes are inherently disruptive—enabling zero-downtime updates in production environments.
7. What is the role of ONES in automating Day-2 network operations?
Day-2 operations such as maintenance, upgrades, and configuration adjustments are simplified by ONES through automated cost-out and cost-in workflows, real-time telemetry, and programmable APIs. This reduces manual intervention, minimizes error risk, and enhances the agility of NetOps teams managing dynamic network fabrics.
8. Why is draining (cost-out) critical in modern data centers?
Draining allows traffic to be safely rerouted from devices undergoing maintenance, upgrades, or experiencing faults—without impacting user-facing services. It supports load balancing, resource optimization, and fault isolation. ONES automates this process, making it repeatable, reliable, and vendor-agnostic.
9. What makes ONES Orchestration suitable for large-scale or hybrid infrastructure?
ONES Orchestration supports multi-vendor, multi-ASIC environments, integrates with tools like Ansible and Grafana, and enables centralized control via API-driven automation. This makes it ideal for large-scale, heterogeneous networks that demand scalability, flexibility, and reliability in automation workflows.
10. Can ONES Orchestration help reduce human error in network operations?
Absolutely. By automating critical tasks like configuration management, provisioning, and service orchestration through standardized APIs, ONES minimizes manual CLI interactions—significantly reducing the likelihood of configuration mistakes, which are common causes of outages in traditional network management.