Abstract
In modern data centers, network observability plays a crucial role in performance monitoring, security, and analytics. However, redundant network traffic can create inefficiencies, leading to excessive processing overhead and degraded system performance. This blog discusses an innovative approach to Network Observability DeDuplication, leveraging filtering, deduplication, and optimized distribution strategies to enhance network efficiency and improve analytics accuracy.
Introduction
As enterprises scale their digital infrastructure, managing high-bandwidth network traffic efficiently is a significant challenge. Duplicate packets from various sources, including TAPs and mirrored configurations (SPAN, ERSPAN), lead to unnecessary data processing, storage, and bandwidth consumption. Network Observability DeDuplication addresses this challenge by filtering irrelevant traffic, identifying duplicate packets, and ensuring optimized data distribution for analytics tools.
Solution Architecture

The proposed Network Observability DeDuplication solution consists of four key components:
Data Sources
- Data Center Fabric: Network traffic is captured and forwarded through physical TAPs and mirror configurations such as SPAN and ERSPAN.
- This traffic contains both relevant and redundant packets that need to be processed efficiently.
Filtering Fabric
- Open Packet Broker Network Operating System (OPBNOS) ensures that only relevant traffic is forwarded, reducing unnecessary processing and enhancing system performance.
- This step helps in reducing computational and bandwidth costs associated with duplicate or irrelevant data.
Core Fabric & Deduplication
- Core Fabric: The filtered traffic is directed towards a high-capacity core fabric (100G-400G) for further processing.
- Aviz Service Node (ASN): A specialized x86 + DPDK-based service node is utilized for high-speed deduplication.
-
Deduplication Process: Traffic is continuously analyzed in real time with a granularity of up to 8 milliseconds, enabling the rapid detection and elimination of duplicate packets. The analysis process begins by inspecting ingress packets for familiarity based on their type and fields. If a packet is found to exist within the customer-defined time frame, it is identified as a duplicate and dropped.
Once the deduplication is complete, the refined traffic is seamlessly reintegrated into the core fabric for further processing and routing. By ensuring that only unique packets are forwarded, this approach enhances resource allocation, reduces processing overhead, and maintains low latency. The result is a streamlined traffic flow that improves data transmission efficiency, enhances application performance, and ensures a smoother user experience across the network. - Configuration Elements:
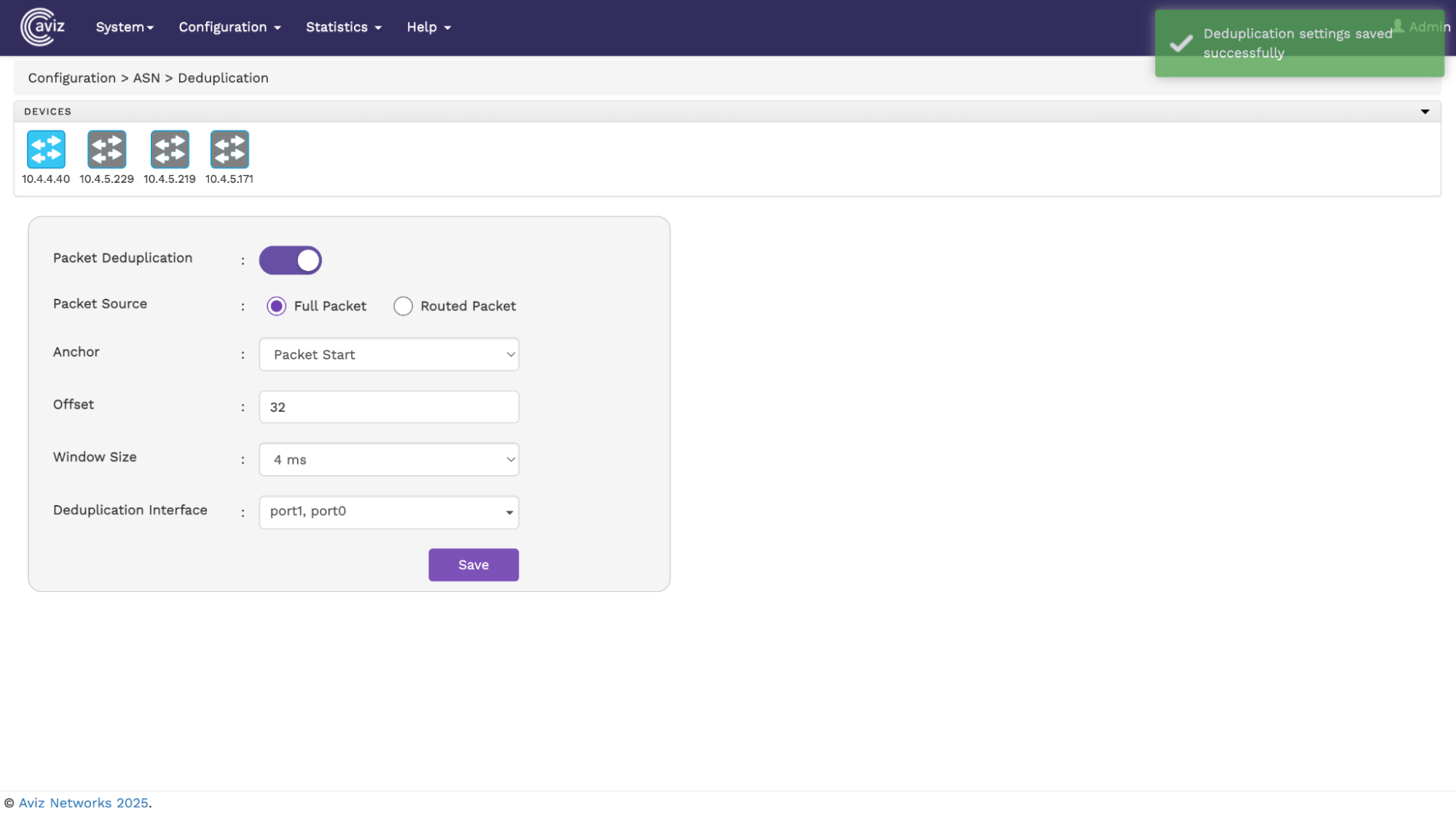
- Packet Source: This defines what data fields to take in while analysing the packet for duplicates. Currently there are two packet source types:
- Full Packet: The packet bytes from start to end, maximum of offset bytes.
- Routed packet: In real time, the packets can be routed across multiple devices/hops. Hence there are chances the duplicate packets can be received to monitoring fabric with different Src MAC/TTL/Checksum fields. This option helps in finding duplicate packets irrespective of Routing parameters.
- Anchor: This tells where to start reading the packet from. The possible values are Packet start ,L3 Start, L4 Start and L4 Payload.
- Offset: To provision how many bytes are considered for duplicate comparison. Allowed Offset is 14 to 128 Bytes.
- Window Size: This config tells the core logic to look for familiar packets in the 2,4,6 and 8ms range currently. If a user for example sets the window size to 6ms, the adjacent packets falling in each 6ms window will be checked for duplicate data.
Distribution Fabric
- The deduplicated traffic is load-balanced and distributed across multiple analytics tools for network monitoring, security analysis, and performance optimization.
- This ensures efficient utilization of analytics resources without redundant data inflating storage or processing costs.
Key Benefits
Performance Optimization
- Reduces the overhead of processing duplicate packets, improving monitoring efficiency by 30 to 50%.
- Enhances the responsiveness of analytics tools by providing cleaner, non-redundant data.
Cost Savings
- Minimizes bandwidth and storage costs by filtering and deduplicating redundant traffic.
- Optimizes computational resources by reducing unnecessary packet processing.
Improved Security & Compliance
- Enhances security monitoring by providing accurate traffic visibility.
- Facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements by ensuring only relevant network data is retained.
Conclusion
Network Observability DeDuplication is a transformative approach to handling large-scale network traffic efficiently. By integrating filtering, deduplication, and intelligent distribution mechanisms, organizations can achieve optimized network monitoring, reduced infrastructure costs, and enhanced analytics accuracy. As data centers continue to evolve, deploying such intelligent traffic management solutions will be key to maintaining high-performance, scalable, and secure network infrastructures.
FAQs
1. What is packet deduplication in data center monitoring?
Packet deduplication is the process of identifying and removing duplicate network packets generated by mirrored traffic sources like TAPs, SPAN, or ERSPAN. It enhances monitoring efficiency by reducing redundant data before it reaches analytics tools.
2. Why do data centers need deduplication for network observability?
Modern data centers generate massive amounts of traffic, much of it duplicated due to mirroring from multiple sources. Deduplication ensures only unique packets are analyzed, which improves accuracy, reduces tool overload, cuts storage costs, and accelerates threat detection.
3. How does Aviz ASN perform real-time packet deduplication?
Aviz Service Node (ASN) uses a DPDK-accelerated engine to scan packets in real time, comparing specific byte ranges within user-defined time windows (2–8 ms). It filters duplicates based on fields like offset, anchor points, and source types (e.g., routed vs. full packet).
4. What are the key benefits of network packet deduplication?
- Performance boost: Increases analytics speed and accuracy
- Cost savings: Reduces bandwidth and storage needs
- Security: Improves anomaly detection by eliminating noise
- Compliance: Ensures clean, policy-aligned data retention
5. How does packet deduplication support scalability in monitoring fabrics?
By removing unnecessary duplicates at the core fabric level, deduplication lowers data volume, enabling seamless distribution across multiple monitoring tools. This improves scalability and ensures high performance even in high-throughput environments.





