TL;DR
- How to design lossless, high-performance fabrics for AI/LLM workloads
- Cisco 8000 series with Silicon One + SONiC explained
- Techniques for RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE v2), Priority Flow Control (PFC), and Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN)
- How Aviz ONES delivers multi-vendor observability and real-time congestion insights
- Validated leaf-spine topologies and blueprints for scalable AI clusters
As data centers evolve from CPU-centric to GPU-centric architectures, building networks that can handle massive AI workloads has become mission-critical. At the recent Cisco and Aviz Networks joint bootcamp, attendees got an inside look at how to design modern, lossless, high-performance networks for AI and LLM workloads.
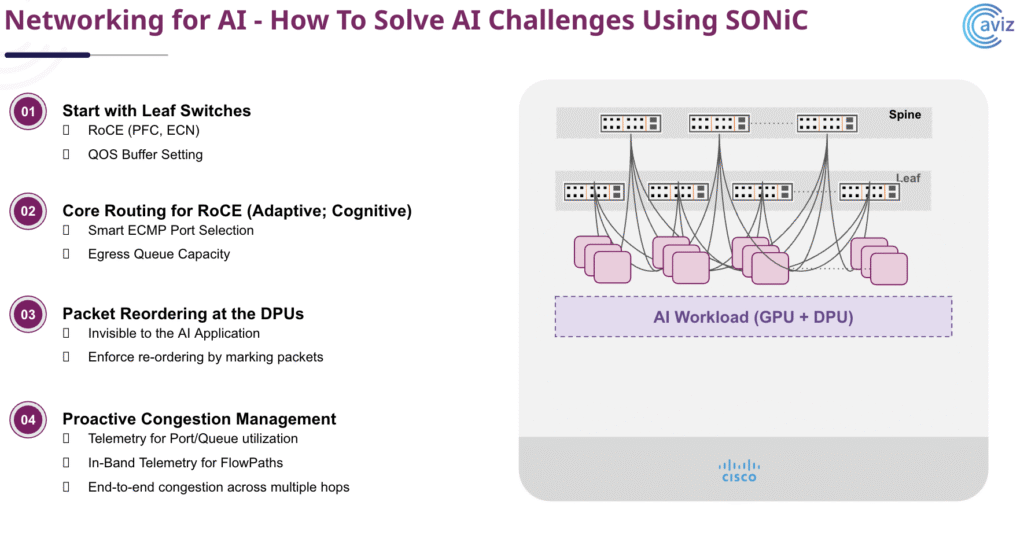
Satish Surani, Director of Product Management at Cisco, showcased how the Cisco 8000 series, powered by Silicon One and SONiC, delivers a flexible, open networking stack designed for today’s demanding AI clusters. Key topics included the importance of RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE v2), Priority Flow Control (PFC), and Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) to maintain low latency and lossless traffic under heavy GPU workloads.
Aviz demonstrated how its Open Networking Enterprise Suite (ONES) and real-time telemetry can monitor and optimize congestion points, validate QoS policies, and provide deep observability across multi-vendor environments.
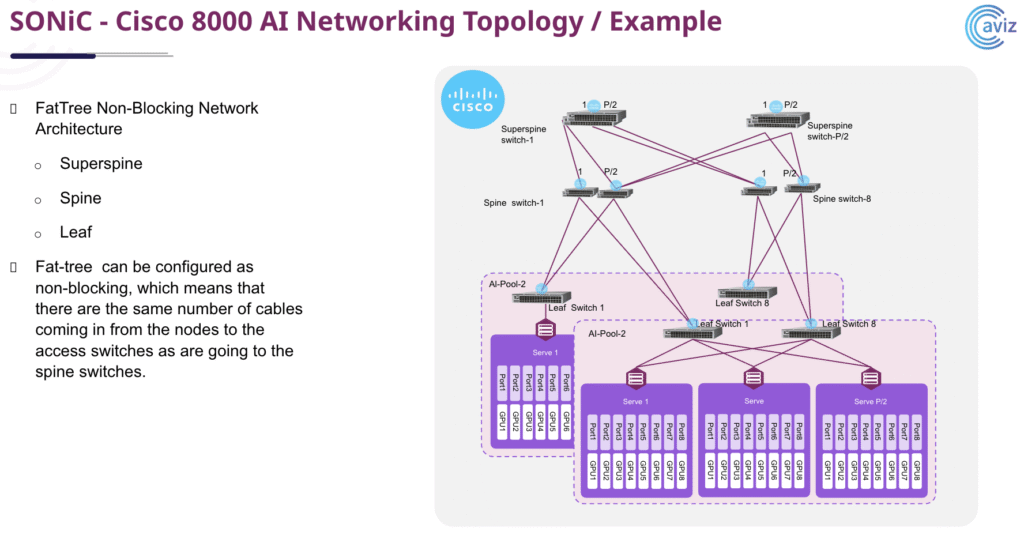
The session also covered best practices for building scalable, non-blocking leaf-spine topologies and how Cisco and Aviz jointly deliver validated blueprints for large-scale AI infrastructure.
As AI clusters grow, open, programmable fabrics with robust congestion management are no longer optional — they’re foundational for faster job completion and predictable performance.
Learn More: Explore Aviz ONES
Watch the full bootcamp on-demand
1. What was the main focus of this joint bootcamp?
This bootcamp explored how to design AI-ready data centers using Cisco 8000 switches running SONiC NOS — and how Aviz ONES delivers observability, congestion management, and telemetry for lossless, high-bandwidth AI workloads.
2. Why is lossless networking so important for AI workloads?
AI clusters require:
- High bandwidth
- Low latency
- Zero packet loss for RDMA flows
Even slight congestion can increase training job completion time. Techniques like PFC and ECN keep traffic lossless and predictable.
3. What is RDMA and why does it matter?
Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) allows data transfer directly between server memory without CPU involvement, which:
- Reduces latency
- Increases throughput
- Optimizes GPU-centric workloads
ROCE v2 (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) was discussed as a practical method for enabling RDMA on Ethernet networks.
4. How does ECN help manage congestion?
Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) marks packets experiencing congestion instead of dropping them outright. End devices then get feedback to slow down traffic rates, preventing packet loss and ensuring consistent AI training performance.
5. What is Priority Flow Control (PFC) and how is it used?
PFC provides lossless service for specific traffic classes. In AI networks, PFC:
- Guarantees no packet drops for RDMA traffic
- Enables mixed traffic without sacrificing critical flows
- Works in tandem with ECN for robust congestion management.
6. How does Cisco’s Silicon One support AI networking?
Cisco’s Silicon One G200 chip powers switches with:
- Ultra-low latency
- High radix (51.2 Tbps capacity)
- Fully shared packet buffers for burst absorption
These features enable massive GPU clusters with efficient load balancing and job completion time optimization.
7. What is the role of SONiC NOS in this architecture?
SONiC provides an open, modular network operating system that customers can fully customize. Cisco 8000 switches run SONiC with enterprise support, ensuring open standards, rapid feature updates, and community-driven innovation.
8. How does Aviz ONES integrate with Cisco hardware?
ONES acts as an agentless observability and orchestration layer:
- Collects multi-vendor telemetry
- Monitors PFC, ECN, and RDMA health
- Visualizes real-time AI traffic versus non-AI traffic
- Automates troubleshooting across leaf-spine and super-spine topologies.
9. What was shown in the factory topology demo?
The live demo featured:
- Cisco 8100 switches configured for PFC and ECN
- Factory topology design with non-blocking bandwidth
- Real-time visibility of congestion points and queue health via Aviz ONES
This demonstrated how to keep AI traffic lossless and optimize cluster efficiency.
10. How does ONES handle multi-vendor, hybrid networks?
ONES is designed for openness:
- It supports SONiC, Cisco XR, Arista EOS, and more.
- Uses standard APIs and collectors — no heavy agents.
- Offers a unified observability dashboard for hybrid and AI fabrics, regardless of hardware vendor.