When it comes to modern networking, what you can’t see can hurt you. At Aviz Networks, we make the invisible visible—before problems escalate. In a recent bootcamp, we explored how deep observability empowers teams to reduce troubleshooting time, achieve compliance, and build more resilient infrastructure. Through a customer case study, a partner perspective, and a full-stack demo, we showed how organizations are moving from reactive to proactive network operations.
What Happens When Visibility Fails? A Real-World Crisis Unpacked
Frank Vincentelli, CTO of managed service provider Integrated IT, shared a powerful story. After upgrading the infrastructure for a mid-market customer, his team faced a major network outage with no clear root cause. Multiple vendors pointed fingers. Logs were incomplete. Visibility was limited.
With Aviz’s platform—including the Open Packet Broker (OPB) and Aviz Service Nodes (ASN)—Frank’s team was able to rule out false leads and identify the actual source of failure.
Because Aviz embeds lightweight agents within switches, telemetry continued even when the network was down. Once connectivity was restored, historical data flowed in, providing the “X-ray vision” they needed.
“The product is excellent—but it’s the people behind it that made the difference, with Aviz, we transitioned from a dysfunctional vendor relationship to one that’s transparent and proactive.”
Frank Vincentelli, CTO of managed service provider Integrated IT
Why Openness Matters: A Partner’s View from the Field

Joel Winland, Field CTO at Source Code, discussed their strategic alignment with Aviz. Source Code, a global system integrator with nearly $1 billion in revenue, builds both edge and cloud-scale infrastructure. What they needed was a software partner as open and flexible as they are.
Aviz fit that need. Built on open-source principles—including full support for SONiC—Aviz allows customers to choose the hardware, NOS, and deployment model that best fits their architecture. No vendor lock-in. No black boxes. Just choice and control.
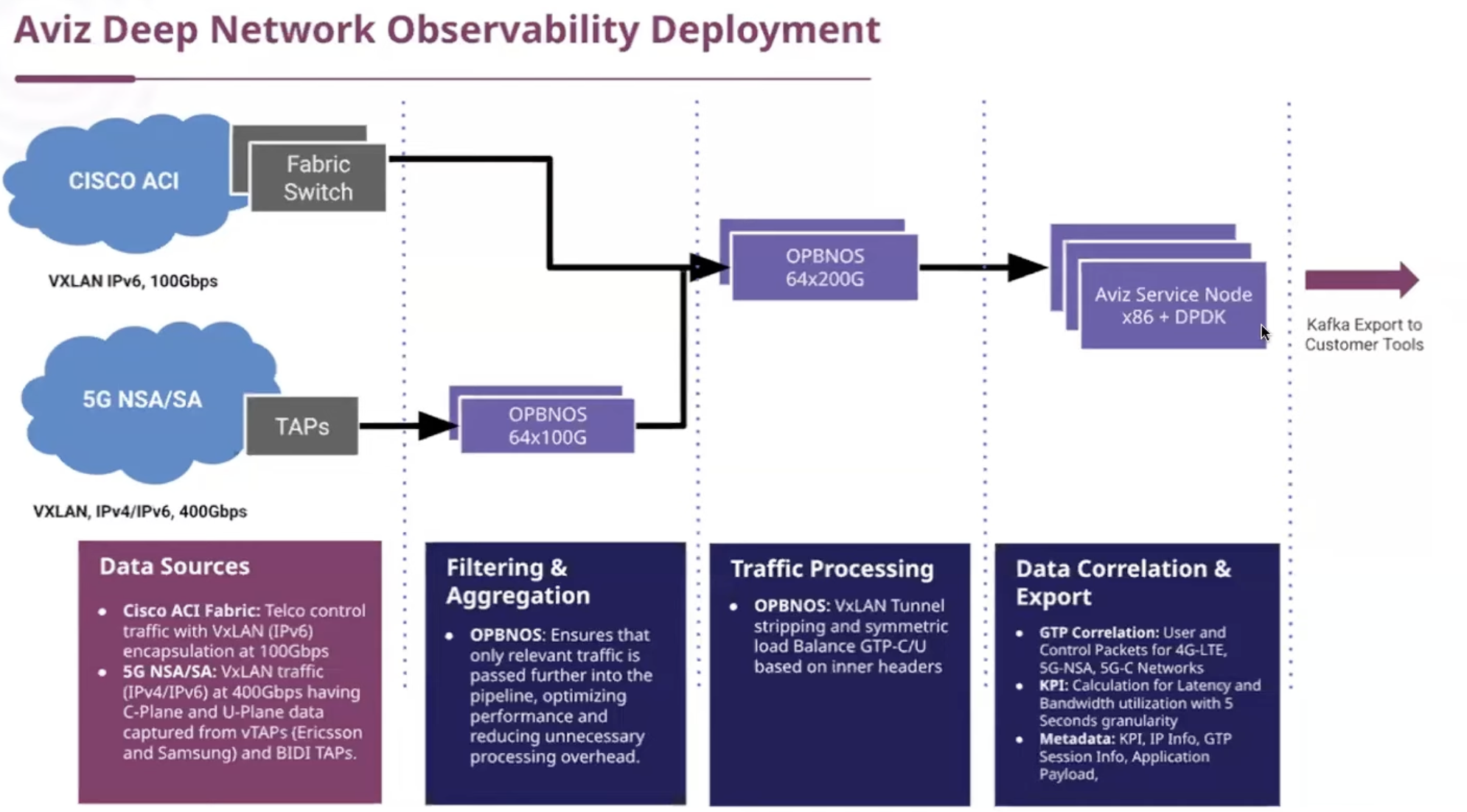
How Does Aviz Deliver End-to-End Observability? A Look Inside the Stack
The Aviz platform is composed of three tightly integrated components:
- Open Packet Broker (OPB): A high-performance, white-box-based traffic management fabric. OPB handles traffic filtering, replication, aggregation, slicing, labeling, and tunneling. It supports granular filtering from L2–L4 and enables advanced capabilities such as GTP header parsing for 5G environments and symmetric load balancing.
- Aviz Service Nodes (ASN): These x86-based software appliances perform deep packet inspection, metadata extraction, KPI generation, application identification, and deduplication. ASN works for both telco (4G/5G) and Enterprise, , providing Application and per-user/session visibility and reducing tool overhead by filtering out redundant, high, and low-risk traffic.
- Network CoPilot (NCP): An AI-powered, on-premises assistant built on open-source LLMs. NCP allows users to query real-time network data using natural language. It’s RAG-enabled, privacy-safe (runs locally), and avoids hallucinations by relying strictly on verified telemetry.
All of this is managed through Flow Vision, a centralized GUI and single pane of Glass that simplifies traffic orchestration, rule configuration, tunnel management, and health monitoring across OPB and ASN nodes.
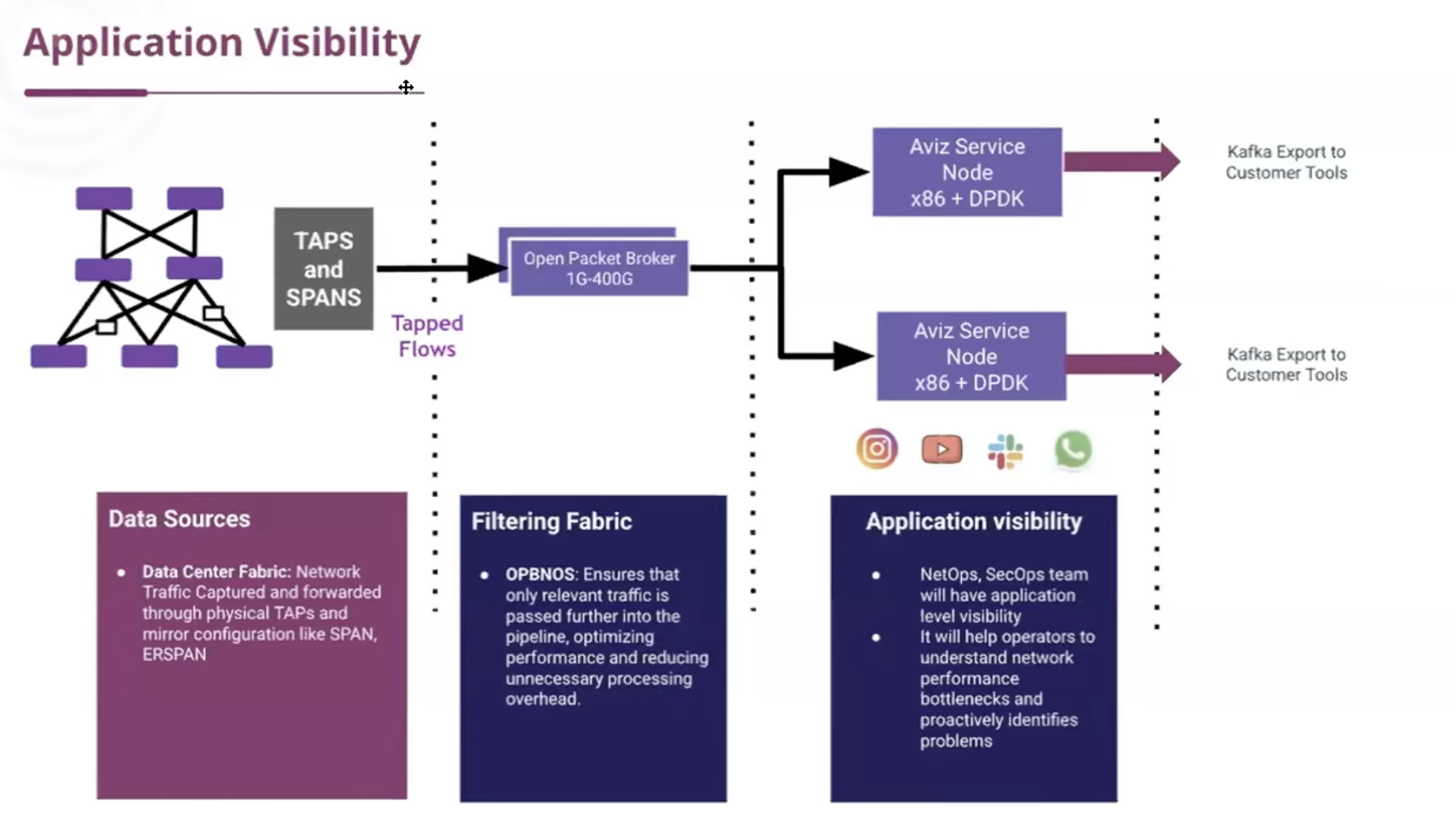
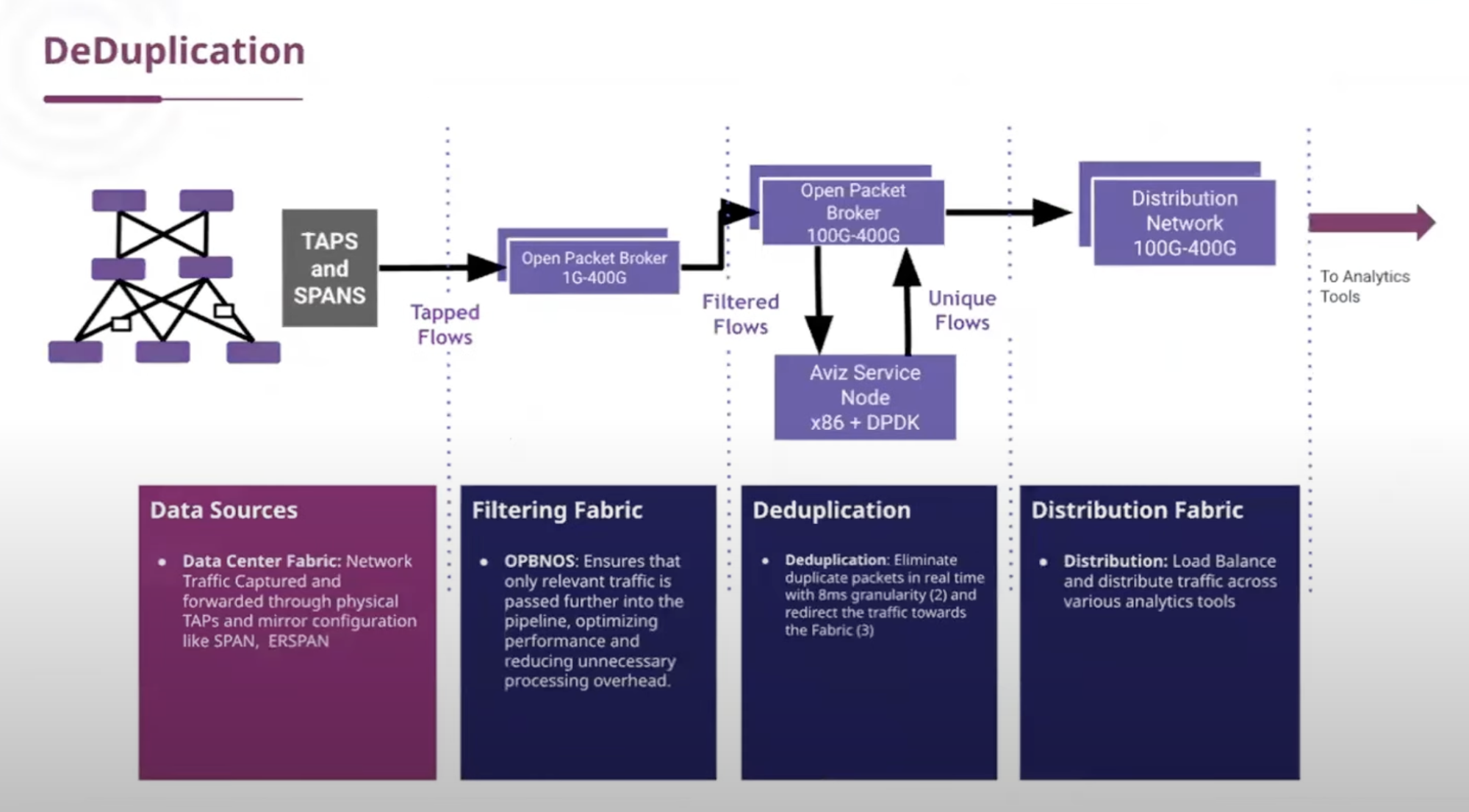
Where Does It Shine? Real-World Use Cases Demonstrated
- Telco Observability: GTP-C and GTP-U correlation at scale, per-user/session KPIs, and 5G SA/NSA analytics.
- Application Visibility: Dashboards for bandwidth usage, OS/device profiling, geolocation, and threat detection.
- Data Center Deduplication: 90%+ reduction in traffic from TAPs before it hits monitoring tools—preserving compute and reducing false positives.
- Natural-Language Queries: Ask questions like “What applications are most used by 5G users?” and receive accurate, traceable answers from NCP.
Is it Built to Scale? Absolutely.
The entire stack is hardware-agnostic and SONiC-ready. OPB supports platforms from Broadcom (Trident, Tomahawk) and NVIDIA (Spectrum 1/2/3). 400G is deployed in production today, and 800G+ support is in active qualification—ensuring that your observability scales with your network.
Conclusion: Visibility Isn’t a Luxury. It’s a Lifeline.
If you’re operating without full network visibility, you’re operating at risk. Aviz Networks offers a scalable, AI-integrated observability stack that empowers NetOps teams to identify issues early, resolve them quickly, and operate with confidence across multivendor environments.
Join our next bootcamp with NVIDIA on June 12 for a deep dive into AI-Powered Networking with Spectrum-X.
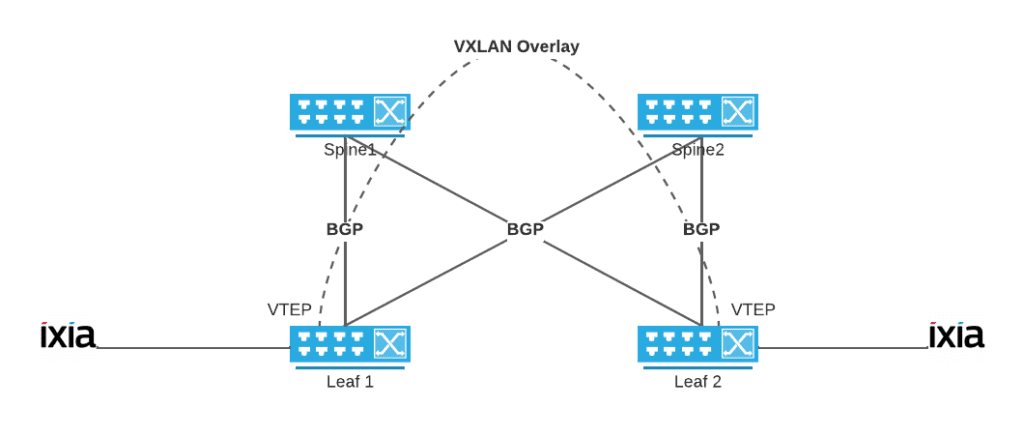
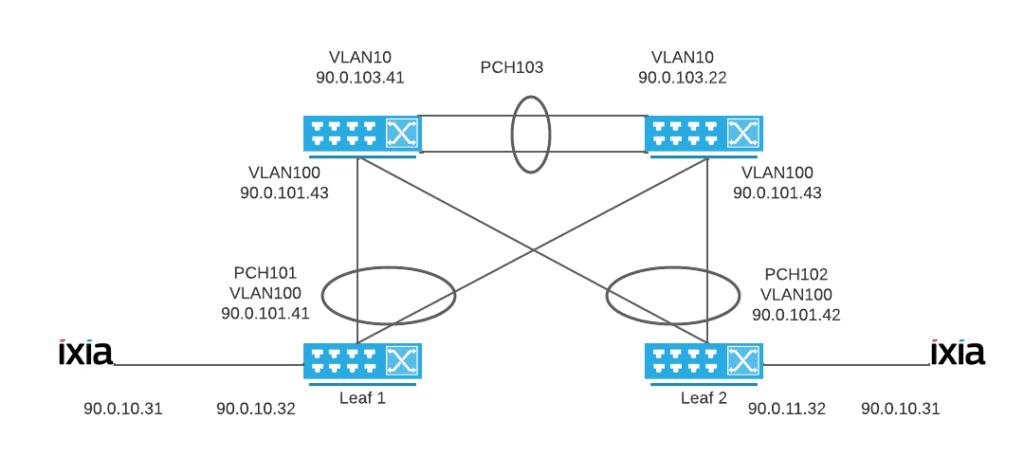
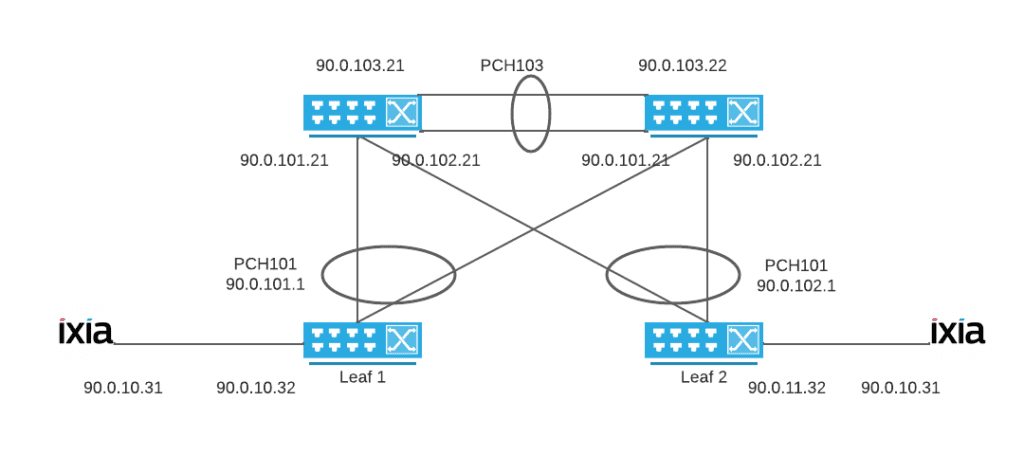
Explore how the Open Packet Broker (OPB) delivers real-time traffic filtering, load balancing, and deep observability across disaggregated environments.